Introduction
In the realm of modern telecommunications, Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) stands as a cornerstone protocol facilitating communication over the internet. Its significance cannot be overstated, particularly in the context of VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) communication and SIP trunking. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the fundamentals of SIP, its functionalities, and its pivotal role in enabling efficient communication in the digital age.
Understanding SIP
Session Initiation Protocol, commonly referred to as SIP, is a signaling protocol used for initiating, maintaining, and terminating real-time sessions involving multimedia elements such as voice, video, and messaging over IP networks. Essentially, SIP serves as the backbone of VoIP communication, enabling seamless interaction between users irrespective of their physical locations.
Key Components of SIP
- User Agents (UA): User agents are endpoints in the SIP network responsible for initiating or receiving communication sessions. They can be software-based applications like softphones or hardware devices like IP phones.
- SIP Servers:
- Proxy Server: Proxy servers act as intermediaries between user agents to facilitate routing of SIP requests. They also provide functions like authentication, authorization, and routing.
- Registrar Server: Registrar servers maintain a database of user locations and addresses, allowing for the resolution of SIP addresses to IP addresses.
- Redirect Server: Redirect servers provide clients with information about the next hop to reach the desired destination.
- SIP Messages:
- INVITE: Used to initiate a session between users.
- ACK: Confirms the successful establishment of a session.
- BYE: Terminates a session.
- REGISTER: Registers the location of a user agent with the registrar server.
Functionality of SIP
SIP operates on a request-response model, where clients send requests to servers, and servers respond accordingly. When a user wishes to initiate a communication session, their UA sends an INVITE request to the SIP server, which then forwards it to the intended recipient. Upon acceptance, the server facilitates the establishment of the session, enabling real-time communication to occur.
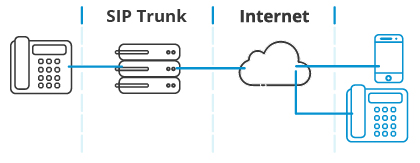
SIP Trunking: Revolutionizing Communication
SIP trunking represents a significant advancement in telecommunications, offering businesses enhanced flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency in their communication infrastructure. Unlike traditional PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) connections, which rely on physical lines, SIP trunking leverages internet connections to transmit voice and data packets.
Benefits of SIP Trunking
- Cost Savings: SIP trunking eliminates the need for costly physical infrastructure associated with traditional phone lines, resulting in substantial cost savings for businesses.
- Scalability: SIP trunks can easily scale up or down to accommodate changing business requirements, providing unparalleled flexibility.
- Enhanced Features: SIP trunking offers a range of advanced features such as auto-attendant, call forwarding, and unified communications, enhancing productivity and collaboration.
- Geographical Flexibility: With SIP trunking, businesses can establish virtual phone numbers with area codes from different regions, allowing them to create a local presence regardless of their physical location.
Implementation of SIP Trunking
Implementing SIP trunking involves several steps:
- Assessment: Evaluate your existing infrastructure and communication needs to determine the feasibility and benefits of transitioning to SIP trunking.
- Selecting a Provider: Choose a reputable SIP trunking provider that offers reliable service, competitive pricing, and robust support.
- Configuration: Configure your network equipment and SIP-enabled devices to communicate with the SIP trunking provider’s network.
- Testing: Conduct thorough testing to ensure seamless integration and functionality of SIP trunking within your organization.
- Deployment: Once testing is successful, deploy SIP trunking across your organization and provide necessary training to staff members.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) serves as the linchpin of modern communication, facilitating the seamless exchange of multimedia sessions over IP networks. With the advent of SIP trunking, businesses can harness the power of SIP to revolutionize their communication infrastructure, unlocking cost savings, scalability, and enhanced features. As technology continues to evolve, SIP remains at the forefront, driving innovation and transforming the way we connect and communicate in the digital age.



